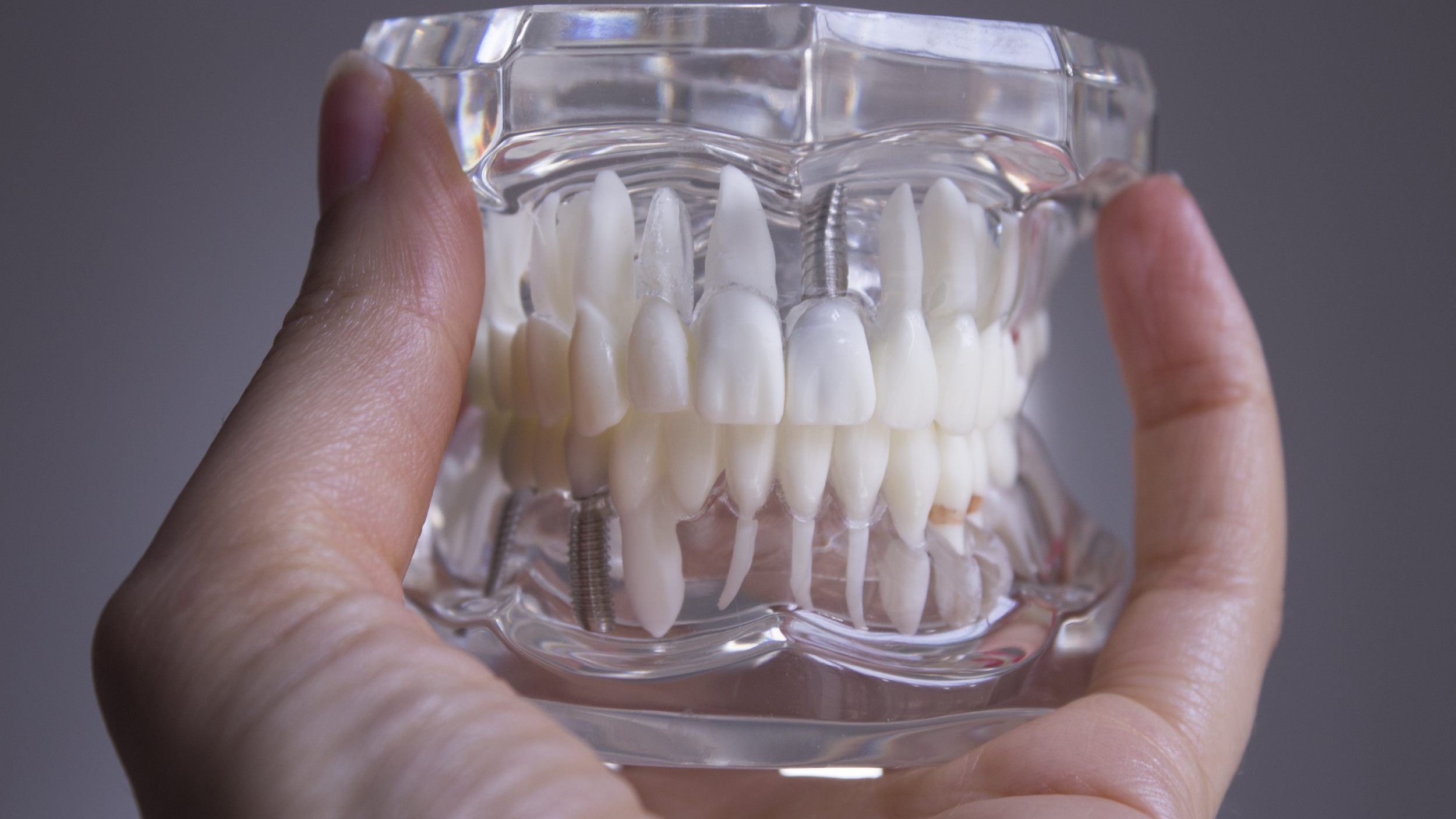
Just as medical computers are a specialization of computers for healthcare, AI dentistry is the application of artificial intelligence to oral health. Today’s article covers four ways the emerging technology is transforming how dentists bring health care to their patients.
AI Dentistry and Detection of Dental Disease
Article Guide
Artificial intelligence has been adopted in all dental specialties:
- Operative dentistry
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery
- Orthodontics
- Periodontics
- Prosthodontics
The most common use of AI dentistry is in detection of pathologies. Bone loss, dental caries (aka tooth decay), and periodontal disease are the most common ones.
Detection is done through radiographic or optical imaging like 2-D and 3-D X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). AI can help by finding the smallest deviations to the patient’s mouth and jaw structure. Then, by analyzing visual images, it can instantly enable dental professionals to see diagnostic results.
This diagnosis of problems in the early stages is very beneficial. Several studies of tumor and cancer detection based on radiographic, microscopic. and ultrasonographic images using AI have shown accuracy at levels the same or even better compared with dentists. AI-powered solutions can empower dental providers to make informed clinical judgments faster, decide the best modalities for their patients, all the while eliminating unnecessary procedures.
Using AI Dentistry in Dental Design
AI is ideal for solving problems in prosthodontics, or that branch of dentistry dealing with the design, manufacturing, and fitting of artificial replacements for teeth and other parts of the mouth. It can be combined with computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) to design onlays, inlays, crowns, and bridges used to solve those problems. These prosthetics can be created with a high degree of accuracy as well as tailor-fit to the patient’s case. Also, algorithms have been designed to predict treatment results, simulating the changes in the patient’s appearance via pre- and post-treatment facial imaging. Dental providers can present the images to the patient for information and reassurance.
AI and Teledentistry
Teledentistry is a subspecialty of telehealth. Thanks to telecommunication technologies, dentists can give dental consultation and treatment planning to patients over remote distances.
Teledentistry can be a lengthy and involved process. For example, while patients can send images of their oral health issues to their dentists, they may have to do reshoots because the images may not be clear or at the wrong angle. This back-and-forth exchange can sometimes take days just to find out if a patient is even eligible for treatment. The result? Patients may abandon the consultation in frustration. Or the delay in diagnosis can potentially worsen their issue.
AI dentistry can speed up this process. First, it can power the image processing and recognition software to guide the patient how to take a photo correctly. Second, it can extract the needed information from the photos and present it to the dentist. Both drastically increase the success rate of each teledentistry consultation.
Australian dentists are already using an image recognition tool called DentalMonitoring in this fashion. Its AI takes the teeth screening sent by the patient’s smartphone and analyzes it. A detailed list of the patient’s gum health, teeth health, and teeth alignment is generated shortly afterwards for the dental health provider to review.
Stress Release through AI Dentistry
Finally, AI can deal with many of the repetitive tasks affecting the healthcare industry as a whole and which has led to burnout among clinicians.
There are two ways this can be done in dentistry. First, the AI can be used to deal with many typical back office tasks. It could, for example:
- Use machine learning (ML) to track patients’ progress and treatment through the provider’s dental practice software like EMR.
- Allow office administrators to flag patients who are at risk of skipping appointments, missing payments, or failing to keep up with treatment plans.
- Make scheduling and rescheduling appointments a breeze to perform. Same is true with proactively sending appointment reminders.
- Ensure a healthy cash flow by decreasing the uncertainty of patient treatment and increase case acceptance. The result is the minimization of disputes and denials by insurance companies and/or governmental health agencies
Automating many of the dental provider’s workflow is the second method. AI can be integrated with voice activation to control many dental medical devices and even equipment like medical grade monitors. As an example, the dentist could bring up the patient’s latest X-ray via vocal commands while treating them. This allows practitioners to multitask which leads to more effective use of their – and the patient’s – time in the chair.
AI dentistry can be extended into the dental chair itself. Useful features such as calculating weight and height, monitoring a patient’s breathing rate, and providing tell-tales of their anxiety levels could save dentists a few extra steps. This frees them to concentrate on treating their pressing dental issues. Voice commands also make infection control simpler since there’s no need to touch any screen surfaces.
Closing Thoughts
Artificial intelligence is making inroads in all fields of the healthcare sector, including oral health (dentistry). Dentists tap AI dentistry to assist them in a wide range of patient care from analysis of pathologies to recording keeping.
Contact an expert at Cybernet if you’re interested in learning more about AI’s potential in dentistry and why this works best with medical computers and tablets.
Join the conversation and connect with us on this and other relevant topics – Follow us Facebook, Twitter, and Linkedin.
Three Major Dentistry Challenges and Possible Tech Solutions
December 27, 2022
Over five thousand years have passed since the first recorded dentist looked into the mouth of a patient. His modern counterparts deal with even greater challenges from increased competition to government regulation.…
0 Comments7 Minutes
4 Ways That AI will Affect Medical Computer Systems
August 28, 2018
The term “artificial intelligence” conjures images straight out of science fiction blockbusters: super-smart machines controlling all aspects of life, and often running wild to destroy their human creators. In reality,…
0 Comments6 Minutes
Why Medical Tablets are the “Swiss Army Knife” of IT solutions
May 25, 2015
Over recent years, healthcare professionals have steadily migrated from traditional workflow platforms to modern alternatives that allow for more streamlined management procedures. The driving force that fuels this…
0 Comments5 Minutes
You Can't
Learn from a Pop-up
But we can deliver knowledge to your inbox!
We dive deep in the industry looking for new trends, technology, news, and updates. We're happy to share them with you.
Knowledge, News, and Industry Updates Right in Your Inbox