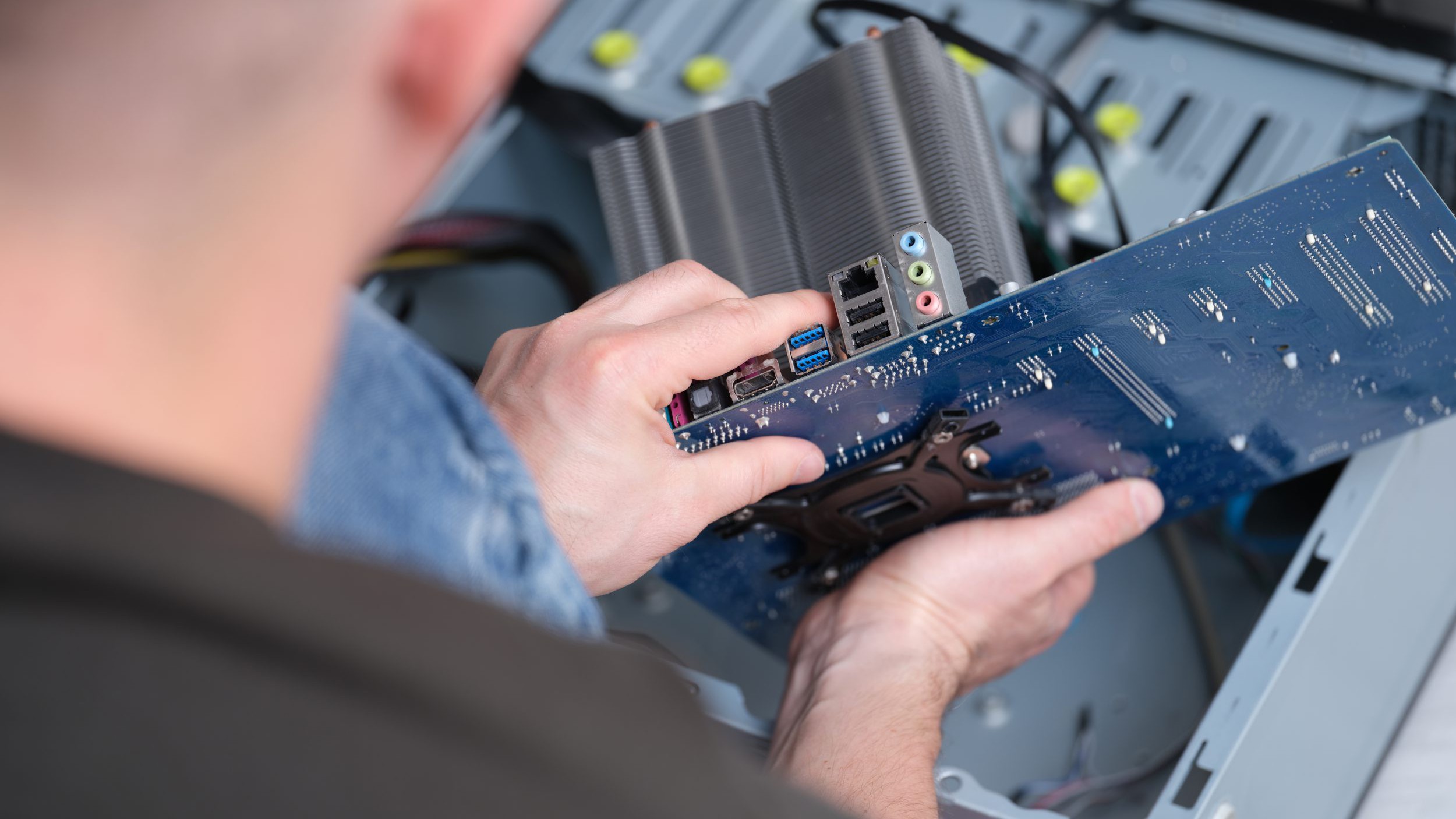
Open almost any PC chassis and you’ll see its cooling system whether it’s a squarish fan unit or the more exotic water cooler. Or no fan at all if your PC uses a fanless design.
What are the similarities? How different are they? This guide aims to answer these questions in the hopes it’ll help you select the right one for your PC needs.
PC Cooling: Is It Necessary?
Article Guide
Overheating the computer can damage the CPU permanently. And without it, the PC is a piece of expensive junk.
Excess heat causes several effects to the computer, none of them are good. We touched up on this in how industrial computers survive tough conditions.
- The electrical resistance of various components will drop. This means more electricity will flow through them than originally designed. This produces more heat and possibly frying the component.
- Heat speeds up the chemical reactions within batteries which shortens both their effectiveness and life.
- The platters making up the computer’s hard disk expand in too much heat. This will damage any data on them perhaps permanently.
- The solder binding the various components onto the motherboard can melt, resulting in the parts falling off.
Heat affecting computers comes from two sources. The first one is from an environment like the freezing winds at an Arctic research station or the scorching deserts surrounding a Middle Eastern oil rig. Computers in both suffer extreme temperatures from their surroundings.
The second source is the computer itself. Today’s machines are built with a lot of silicon-based parts. These require electricity, with the amount completely dependent on the part’s function. Electricity that is lost due to inefficiencies in design and materials become heat. Certain users such as gamers also deliberately increase processing speed through a process called “overclocking” which releases even more heat.
Most off-the-shelf computers can operate up to 150 degrees Fahrenheit, or 70 degrees Celsius and still function for brief periods of time. Extended uses at these temperatures will cause the above damage over time. PC Manufacturers rarely allow their machines to reach such temperatures using built-in fail-safes (called automatic thermal-throttling) to slow or even shut them down before permanent damage can occur.
Using Air or Water to Cool a PC
A computer’s cooling system’s aim is to keep the machine at optimal temperatures. This is done by:
- Exhausting hot air within the case which reduces the interior temperature.
- Keeping a single component or small area cool within the computer. This is called “spot cooling” and is done using an air or liquid cooler. Components commonly targeted include the CPU and the graphics processing unit (GPU).
Fan Cooler: Cooling the Entire PC

Most PC cooling uses fans. Computers can have multiple fans, especially those in a tower case or chassis.
As the name implies, cooling the computer by fan is achieved by arranging those fans so that air flows through the case in as direct a path as possible. The most common way to achieve the desired airflow is by placing air intake fans on the front of the case with exhaust fans either on top, at the rear, or both. This arrangement draws fresh air to cool the interior and pushes heated air out.
Spot Cooling the CPU:
Several technologies are used to perform spot cooling on the CPU. The most common are the use of air coolers and water cooling.
Air Cooler
The fan unit on the CPU is called an “air cooler.” It makes direct contact through a heat plate or base plate. When the CPU warms up, that heat is transferred to the plate, which is composed of several different heat-conductive and dissipative materials like aluminum, copper, and nickel.
Heat is drawn from the plate away through the attached heat pipes. They do so using the gas or liquid within them. The pipes are connected to a heat sink. This blocky structure, which looks like a row of flat, square plates, is also composed of heat-conductive and dissipative materials. The heat is radiated and dissipated out through them as covered in depth in Fanless Cooling: How It Works and Why You Need it. An attached fan moves air over the heat sink to speed up the PC cooling process.
The air cooler is the most common method of spot cooling for computers, especially off-the-shelf brands.
AIO Cooling
The water cooler, as its name suggests, uses water to cool the CPU. That is because water is much better than air in absorbing heat without dramatically increasing in temperature. Water coolers also go by the name of all-in-one (AIO) liquid coolers.
An AIO cooler functions similarly to an air cooler. There are two major differences:
- The water cooler’s heat pipes are attached to tubes connected to a pump, which actively pushes water through the unit in a circular fashion.
- The heated water goes through a radiator where the heat is radiated away. The now cooled water circulates back into the PC cooling system. The attached fan can draw in cool air from outside the chassis to cool the radiator, or push air through the radiator and out of the case to keep the temperature from increasing.
The Advantages, Disadvantages of Air and AIO Cooling
So which system works best for a PC? Unsurprisingly, it depends on several factors. Five are covered here.
- Airflow
It shouldn’t be a surprise that airflow is very important to air coolers. Computers with such a pc cooling system should be located in a well-ventilated space. This allows more air to be pulled in to cool down the heat sink.
Speaking of heat sinks, the adage of “larger is better” applies with larger ones and/or those with more fins better able to keep the CPU cool. Air coolers with more heat pipes can also draw more heat away from the CPU as well.
Cooling via AIO is a good option for those places with restricted airflow like a room crowded with minimal ventilation. Small compact form PCs (see below) with few multi-fan options may also benefit from AIO.
- Budget
Air coolers and their case fans are also more affordable than AIO coolers. Expect to pay at least double for a liquid cooler. AIO coolers are also more complex to install in a PC and require greater maintenance because of the pump, tubing, and water. There’s also the risk of leakage which can severely damage a PC.

- Noise
Fans are a common source of noise in computers along with hard disc drives and even the chassis. Parts from blade design to performance like fan speed affect noise levels. Users concerned with fan noise should consult with the manufacturers, remembering that none can match that of fanless design (see below).
AIO coolers have similar issues. In addition, water cooler pumps can be noisy.
- Small form factor PC
Air coolers work best with maximized airflow. Larger chassis means more air to get rid of heat. Small compact form PCs, many of which are used in the industrial plants and factories, have less room for air to get rid of heat or to install additional fans.
Spot cooling systems may also be too big for a PC chassis. Purchasing an air cooler that is too large could prevent the case from closing or even block other components from fitting properly. Every PC case is rated for a maximum CPU cooler height that it can support.
AIO cooling may not be much better. This is because the radiator may be too large or there may not be enough space to run tubes to the CPU.
- Motherboard socket
Each CPU sits in a socket on the motherboard to connect and control the rest of the PC. Motherboard designs are extremely specific to both CPUs and other peripheral devices. It’s important then that the PC cooling unit is compatible with the exact processor socket of that motherboard.
PC Cooling Without Fans: Fanless Design
Both air and liquid cooling systems draw heat away from a computer’s heat sink. Several manufacturers have ditched both systems entirely, relying instead on the heat sink itself to cool the CPU.
This method offers several advantages:

- Costs are lower since there is no fan or pump system to power.
- Less electricity to power the PC which also means less heat.
- Smaller computers like small form factor PCs are more possible since there’s no need for air to cool the interior or a large radiator to be attached to the exterior.
- Many settings like warehouses have particulates in the air. These can get sucked into a computer by fans and wreak havoc on components. Industries like manufacturing use industrial panel PCs with fanless design to prevent such costly damage.
- Pathogens like air-borne bacteria can be spread by fanned cooling systems which are dangerous in places like hospitals. This is why staff use fanless medical computers in close contact with patients.
- Shock and vibration like dropping a medical tablet can damage fans and water cooling systems. Fanless systems, which have no moving parts, have no such issues.
The main disadvantage of fanless PC cooling is they cannot dissipate heat fast enough in modern computers. Most can deal with temperatures up to 122 degrees Fahrenheit or 50 degrees Celsius. Today’s CPUs can easily reach and even exceed such figures especially during intensive applications like number crunching or video game play. Manufacturers of fanless PCs have been able to work around this limitation with use of industrial grade parts and lower power requirements like in Power over Ethernet.
Closing Thoughts
PC cooling is an important part in computer design since too much heat can cause damage, some of which may be permanent. The CPU, or the brain of the computer, especially generates a large amount of heat. If you’re looking to keep your PC cool for personal use or for your company’s networks, contact a representative from Cybernet on the right PC cooling system for you.
Also follow Cybernet on Facebook, Twitter, and Linkedin to stay up to date on this and other relevant topics.
Advancing Technology: 3 Reasons Why Your Next Medical PC Should Be Waterproof
April 9, 2015
Computers have become ubiquitous in the professional arena – and particularly in the healthcare industry. Medical grade PCs are relied upon to process EMR software and patient cases in an efficient manner. Given the…
0 Comments4 Minutes
Why Fanless Medical Computers are a Must for the Medical Profession
July 9, 2015
The enterprise industries and the healthcare profession have been greatly affected by the increasing use of all-in-one computers and similar devices. The healthcare profession has grown to rely more and more on medical…
0 Comments5 Minutes
Does Better Cooling in a PC Improve Performance?
April 12, 2022
Not only does a cool computer work better, a hot computer is a sign of imminent–and expensive–damage. PCs generate heat, which slows performance and even damages components over time. Cooling systems keep PCs alive in…
0 Comments9 Minutes
You Can't
Learn from a Pop-up
But we can deliver knowledge to your inbox!
We dive deep in the industry looking for new trends, technology, news, and updates. We're happy to share them with you.
Knowledge, News, and Industry Updates Right in Your Inbox